Understanding High Blood Pressure: The Silent Health Threat You Need to Know
High blood pressure, often referred to as hypertension, is a widespread health condition that affects millions of adults worldwide. The alarming fact is that many people might be living with this serious condition without even realizing it, as symptoms can frequently remain undetected. This lack of awareness is particularly concerning because untreated hypertension can lead to severe health complications, particularly heart disease and stroke. Regular blood pressure screenings are essential to help individuals monitor their levels and take proactive steps to maintain a healthy range.
Implementing manageable lifestyle changes can dramatically enhance your ability to control blood pressure levels. Simple yet effective modifications, such as incorporating a nutritious diet that is abundant in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, alongside ensuring adequate and restful sleep, can significantly contribute to maintaining your blood pressure within safe limits. These positive lifestyle adjustments not only promote cardiovascular health but also boost your overall well-being, making them essential for anyone looking to improve their health.
 Blood Pressure Explained: Importance of Monitoring and Measurement
Blood Pressure Explained: Importance of Monitoring and Measurement
Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels, primarily driven by the heart’s pumping action. This crucial measurement indicates how effectively blood circulates throughout your body and the level of resistance it encounters as it moves through arteries. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure level is vital for overall health, as elevated readings can lead to serious health implications, including organ damage and cardiovascular complications.
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is represented by two critical figures:
- Systolic Pressure – This is the top number, indicating the pressure in your arteries during heartbeats when blood is pumped out.
- Diastolic Pressure – This is the bottom number, reflecting the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats.
For example, a reading of 120/80 mmHg indicates a systolic pressure of 120 and a diastolic pressure of 80, which is generally recognized as normal and healthy.
Understanding the Causes and Risks Associated with High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure may develop due to a variety of factors, often linked to narrowed arteries that increase resistance to blood flow. This increased resistance can result in elevated blood pressure levels, which places significant strain on essential organs, including the kidneys, heart, brain, and eyes. Over time, if hypertension is left unmanaged, it can lead to serious health complications, particularly those related to cardiovascular conditions, which are among the leading causes of death globally.
Blood pressure readings can fluctuate due to various reasons, and healthcare professionals categorize them based on established guidelines:
Low blood pressure – 90/60 mmHg or below
Normal blood pressure – Ranges from 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg
High blood pressure – 140/90 mmHg or higher
A reading between 120/80 mmHg and 140/90 mmHg indicates a potential risk of developing hypertension in the future. However, it’s important to note that individual blood pressure norms can vary, so it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider to understand your specific limits and risks.
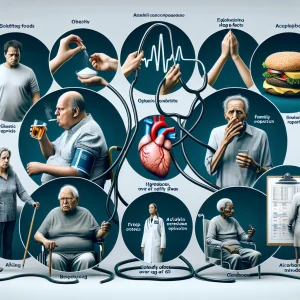 Exploring the Key Risk Factors for High Blood Pressure Development
Exploring the Key Risk Factors for High Blood Pressure Development
There is no single cause of high blood pressure; rather, it is influenced by multiple risk factors that can contribute to its onset. Some significant risk factors include:
- Being overweight or obese – Excess body weight can increase the strain on the heart and blood vessels.
- Smoking – Tobacco use can damage blood vessels and lead to increased blood pressure.
- Consuming a high-salt diet – Excessive sodium intake is linked to elevated blood pressure levels.
- A family history of hypertension – Genetics can play a significant role in an individual’s risk.
- Excessive alcohol consumption – High intake of alcohol can raise blood pressure.
- Lack of sleep – Poor sleep patterns can negatively affect blood pressure regulation.
- Inadequate physical activity – A sedentary lifestyle is a risk factor for hypertension.
- Aging, particularly over 65 – The aging process can lead to increased blood pressure.
- Being of Caribbean or African descent – Certain ethnic groups are at higher risk for high blood pressure.
Many of these risk factors can be modified through proactive lifestyle changes. In rare cases, high blood pressure may also be linked to underlying medical conditions or specific medications, affecting about 1 in 20 individuals. These conditions can include:
- Thyroid disorders – Hormonal imbalances can affect blood pressure regulation.
- Kidney diseases – Impaired kidney function can lead to hypertension.
- Diabetes – This condition can cause damage to blood vessels, increasing blood pressure.
- Use of steroids – Certain medications can impact blood pressure levels.
- Hormonal contraceptives – Some birth control methods can influence blood pressure.
- Recreational drugs, like cocaine – Substance abuse can lead to significant increases in blood pressure.
Identifying the Often Overlooked Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
One of the most significant challenges with hypertension is that it often presents without clear symptoms, which can lead many individuals to remain unaware of their condition. In the UK, it is estimated that around 25% of adults unknowingly live with high blood pressure. The only definitive method to assess your blood pressure status is through regular testing.
You can have your blood pressure checked at various locations, including:
- Your GP’s office or with a healthcare professional – simply ask for a blood pressure check during your visit.
- Many local pharmacies offer blood pressure monitoring services.
- Some workplaces provide health screenings that include blood pressure checks.
- At home, using a personal blood pressure monitor can help you track your levels regularly.
 Proven Techniques to Effectively Lower Your Blood Pressure
Proven Techniques to Effectively Lower Your Blood Pressure
Considering that lifestyle choices play a significant role in the development and management of high blood pressure, making informed changes can help reduce your risk. Here are four essential strategies you can adopt:
Engage in Regular Physical Activity for Heart Health
Incorporating consistent exercise into your daily routine is vital for supporting the health of your heart and blood vessels, ultimately aiding in the reduction of blood pressure levels. Excess weight can place unnecessary strain on your heart, causing it to work harder to circulate blood. By committing to regular physical activity, you can achieve weight loss and enhance your cardiovascular fitness, both of which are essential for lowering blood pressure effectively.
Embrace a Heart-Healthy Diet for Better Blood Pressure
Adopting a well-balanced diet that prioritizes whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, can significantly contribute to lowering blood pressure. Since high sodium intake is known to elevate blood pressure, reducing salt consumption is crucial. The NHS recommends limiting salt intake to less than 6g per day, roughly equivalent to one teaspoon. It is beneficial to decrease the consumption of processed foods that are high in salt and to utilize herbs and spices for flavoring meals instead.
Manage Alcohol Intake for Healthier Blood Pressure Levels
Cutting back on both the amount and frequency of alcohol consumption can have a substantial impact on managing blood pressure levels effectively. Incorporating alcohol-free days into your weekly routine and spacing out drinking days can be beneficial for your health. While the NHS suggests a maximum of 14 units of alcohol weekly—which equals approximately 7 pints of 4% ABV beer or 7 glasses of 175ml wine—it is important to note that you do not have to reach this limit consistently.
Ensure Quality Sleep for Optimal Blood Pressure Control
Consistently poor sleep patterns can increase the risk of developing high blood pressure. The NHS recommends aiming for 6 to 9 hours of quality sleep each night to maintain overall health and proper blood pressure regulation. Establishing a calming bedtime routine and creating a conducive sleep environment can significantly enhance your sleep quality, which in turn supports healthier blood pressure levels.
Presented By: Private Blood Pressure Tests
The Article Blood Pressure Test Explained: What You Need to Know Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com
Comments
One response to “Blood Pressure Test: Key Insights You Should Know”
I really appreciate this deep dive into hypertension; it’s such an important and often overlooked topic. It’s interesting how you mention that many people are unaware they’re living with high blood pressure. It reminds me of a friend who only found out during a routine check-up, despite feeling perfectly fine. It really shows just how vital regular screenings are.